 FTPPCC Skill Development Institute
FTPPCC Skill Development Institute [email protected]
[email protected] 7018040887
7018040887

COMPUTER DEFINITION
The word computer comes from the word "compute" which means, "to calculate". A computer is an electronic device or machine that can perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc. as well as logical operations like comparisons at very high speed. A computer is also called a "Data Processor" because it can store, process, and retrieve data whenever desired.
FULL FORM OF COMPUTER
C - COMMONLY
O- OPERATED
M- MACHIENE
P - PARTICULARLY
U- USED FOR
T -TRADE
E- EDUCATION
R- RESEARCH
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTER
A computer is equipped with number of characteristics that helps it to handle the different problems more efficiently. Some of the main characteristics are:
(i) Accuracy
Computer system always produces accurate results with valid data and instructions.
(ii) Speed
A computer performs operations with very high speed. It can process millions of instructions in fraction of seconds.
(iii) Large Storage Capacity
A computer has large storage capacity. It can store large volume of data. We can store any kind of data in computer's storage. This data can be text, picture, sound, video etc.
(iv)Versatility
A computer is a versatile machine. It can perform a number of jobs depending upon the instructions fed to it .
(v) Reliability
Computerized storage of data is much more reliable than the manual storage.
(vi) Diligence
Unlike human beings, the computer can work continuously without getting tired.
(vii) Automatic
A machine that works itself without any human involvement is said to be an automatic machine.
(viii) Source of Entertainment
Today, computer has become a great source of entertainment.
(ix) Cost Effectiveness
Computers reduce the amount of paperwork and human effort, thereby reducing costs.
(x) No Intelligence
A computer has no intelligence of its own. It depends upon user's instructions for any kind of task.
(xi) Health Issues
Prolonged or Improper computer use can lead to injuries or disorders of the hands, wrists, elbows,eyes, necks, and back. Computer users can protect themselves from these health risks through proper workplace design, good posture while at the computer, and appropriately spaced work breaks.
HISTORY OF COMPUTER
The development of the modern day computer was the result of advances in technologies and man's need to compute. History reveals a clear pattern in the evolution of computers.
(a) Abacus
A manual calculating device mainly used to perform addition and subtraction. It is one of the earliest counting devices consists of a frame set with roads on which balls or beads are moved. Simple addition and subtraction were carried out rapidly and effectively by positioning the beads appropriately, It is still a very common device in China.
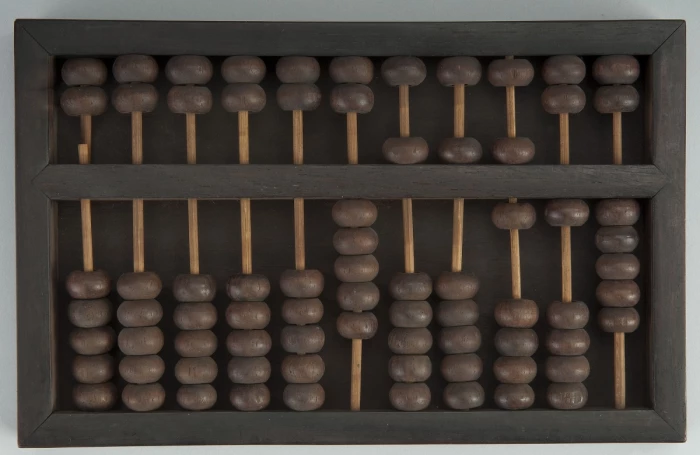

FULL FORM OF ABACUS
Abundant Beads Addition Calculation Utility System.
(b) Napier Bones

Napier's Bones, also called Napier's rods, were invented by John Napier (1550- 1617),
a Scottish mathematician and scientist. The 'bones' consist of a set of rectangular rods,
each marked with a counting number at top, and the multiples of that number down their lengths.
(c) Pascaline
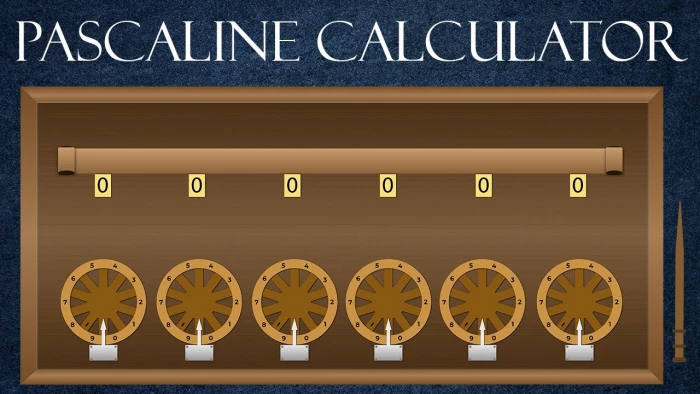
Pascaline, also called Arithmetic Machine, the first calculator or adding machine was
designed and built by the French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal in 1642.
(d) Difference Engine
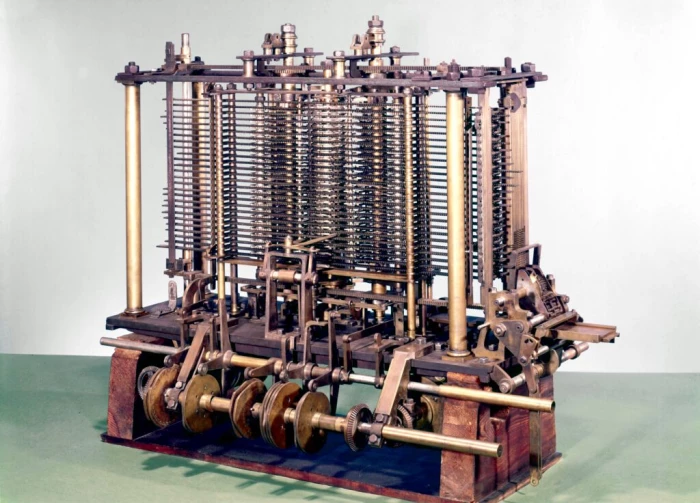
The Difference Engine, designed in 1820s by British mathematician Charles Babbage to perform calculations.
(e) Analytical Engine
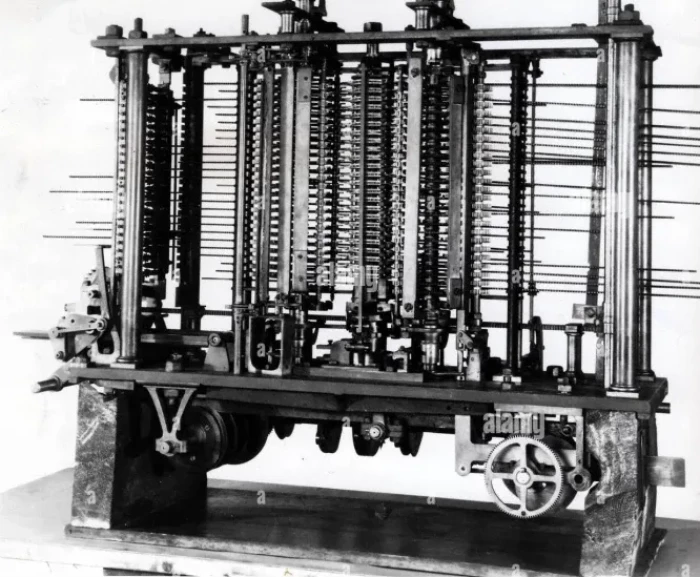
The Analytical Engine was the world’s first general-purpose computer designed in
1830s by the British mathematician Charles Babbage. After his Difference engine
failed its test, Babbage started the design of the Analytical Engine. The Analytical En-
gine Introduced a number of computing concepts still present in modern computers
also. The Analytical Engine was much more than a calculator, it was capable of perfor-
ming comparisons and modifications to a stored data value.
(f) Hollerith’s Tabulating Machine
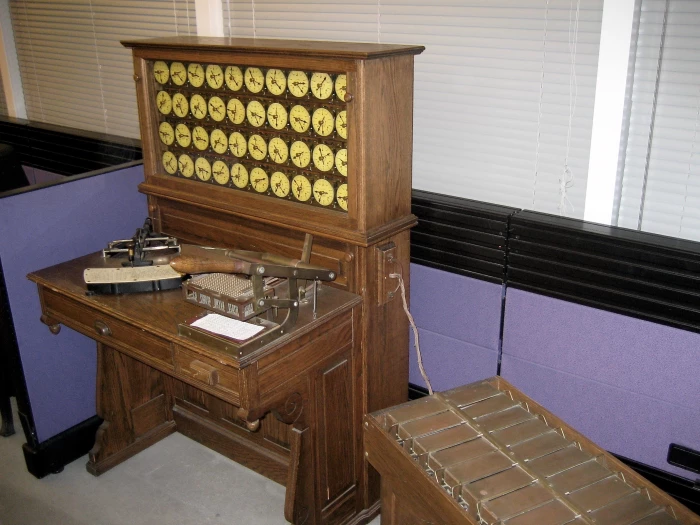

The first automatic data processing system used to count the 1890 U.S. census. This machine was developed by Herman Hollerith, an American mathematician.
FULL FORM OF IBM
International Business Machines (IBM)
(g) Mark- I Computer (1937-44)
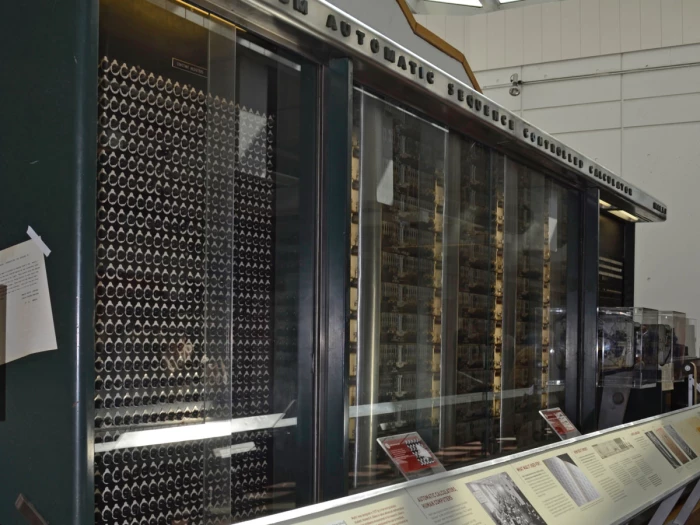

The Mark – I computer also called the Automatic Sequence Controlled
Calculator was first fully automatic calculating machine developed in1937.
It was developed by Professor Howard Aiken of Harward University in collaboration with IBM.
(h) The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (1939-42)

The Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC) was the first electronic digital machine
developed by Dr. John Atanasoff. It used vacuum Tubes and capacitors for internal logic and storage respectively.
(i) The ENIAC (1943-46)
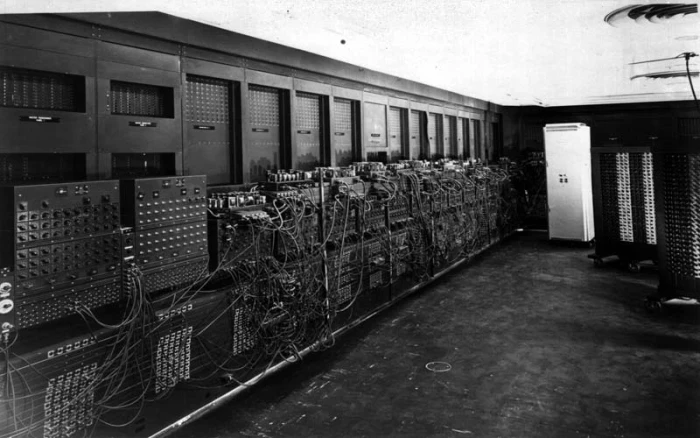
The ENIAC (Electronic, Numerical, Integrator, Analyzer and Computer) was
the first general-purpose electronic computer development by Prof. J Presper
Eckert and Prof. John Mauchly in1943. It used more number of vacuum tubes (approx.19000). It was big in size and very limited storage capacity.
(j) The EDVAC (1946-52)
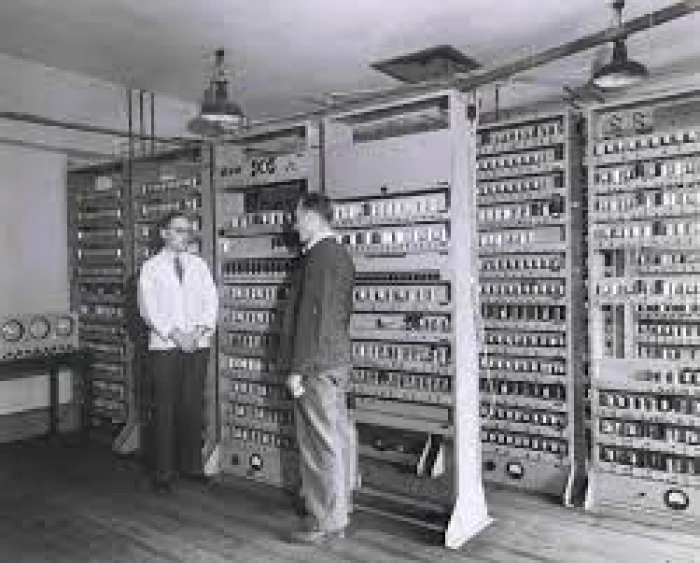

The EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer) was the first
project to build a computer that could store data and instructions
in the binary form (0-1) instead of decimal numbers used by a human being.
(k) The EDSAC (1947-49)

The EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator) was developed
by a group of scientists headed by the Prof. Maurice Wilkes. This machine could
perform the arithmetic operations at a very high speed in order of nanoseconds
(10-9 seconds).In this machine, addition operation was accomplished in 1500
microseconds and multiplication operation in 4000 microseconds.
(l) Manchester Mark I (1948)
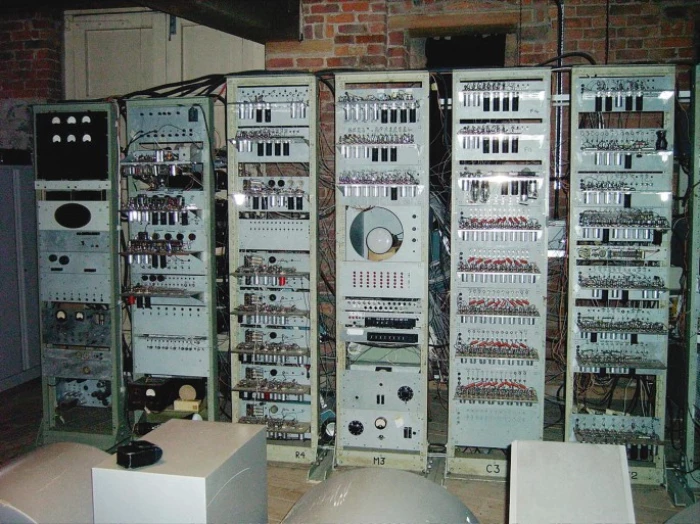

The Manchester Mark I was one of the earliest electronic computers and the first electronic stored
program computer, built at the University of Manchester in England, in 1948. It was also called Manc-
hester Automatic Digital Machine, Or MADM.
(m) The UNIVAC I (1951)
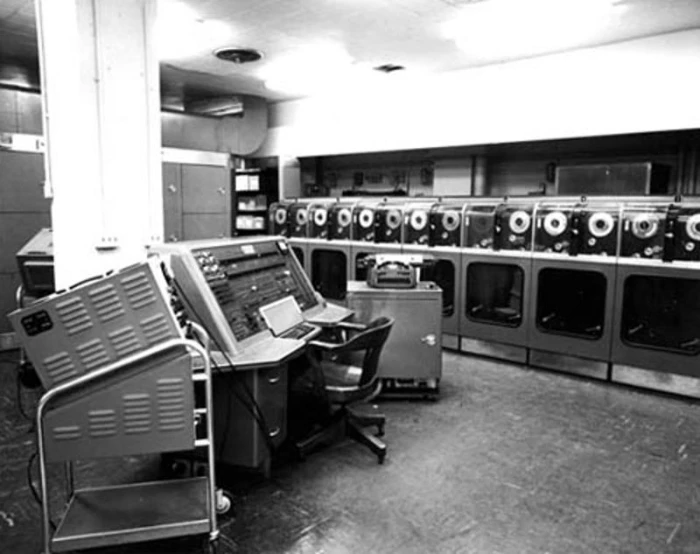

The UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) was the first commercial computer made in the United States.It was designed principally by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, the inventors of the
ENIAC.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
There are various methods on which the computers can be classified. The classification may depend on size, working principles, purpose, technology, area of application, generations etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS BASED ON SIZE
Computers can be classified by their physical size and appearance. By size, we can classify computers into following types:
Micro Computer
· A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer with a microcomputer as its central processing unit.
· A microcomputer is a computer designed for individual use.
· In microcomputers, microprocessor is connected with primary memory (RAM & ROM), input output and secondary storage devices,
· Microcomputers are supported by single user operating systems.
Mini Computer
· Mini computers are general purpose computers, which are more expensive than the microcomputers.
· They also use 16 bit or 32 bit microprocessor as their main CPU. Intel80386,80486 and Pentium are some processors of these computers.
· They can support multiple input-output devices.
· A large numbers of computers can be connected to a network with a mini computer acting as a server.
· Mini computers can be used for systems like- ticket reservation or banking.
· Most commonly used operating system on such computers is UNIX.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTZlk4iv4bY